Utilization of Heterogeneous TPS Patterns for Optimizing Stratified Sampling in Quick Count
Abstract
The process of quick count of election results requires the selection of the right method in order to produce predictions that are close to the actual value at low cost and fast counting time. Starting with the technique of determining the number of respondents (voters), along with a list of polling stations that must be occupied by Quick-Count volunteers, one of which depends on the computational method used. Until it culminates in determining the initial data grouping pattern between Heterogens groups represented by the Stratified Field Sampling (SFS) Method. The research data was obtained from the web vote count results of the 2019 Presidential & Vice Presidential Elections of Jakarta. And the use of optimization methods in SFS produces accuracy values. The peak of effectiveness and efficiency of a Quick Count process is at a confidence value of 99%, Margin of Error 0.01%, with the number of polling stations selected 0.21% of the population. And the SFS method provides average results that are closer to the actual value of 3%. Keywords : Quick Count, Stratified Sampling, Margin of Error, Confidence Level, Polling Station (TPS).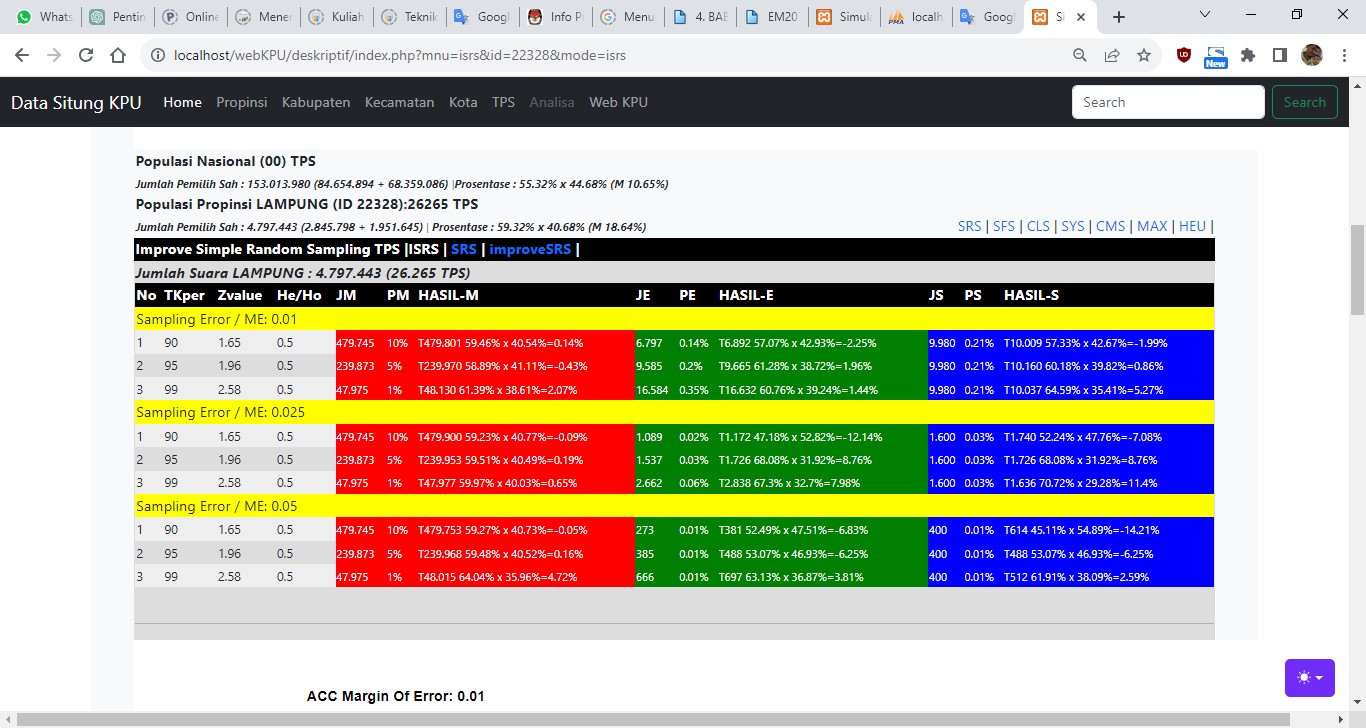
Published
2024-06-30
Section
Artikel

